Cathodic Disbondment Testing
The disbondment test is a simple way of assessing the effectiveness of the bond between the protective coating and the metal structure that it is designed to preserve.
Steel structures such as pipes and tanks that are submerged are usually protected by coatings bonded to its surface and by cathodic protection. Many pipelines are protected by ICCP (Impressed Current Cathodic Protection) as are large Boats and Ships. Any protective coating using this kind of protection will need to be evaluated for Cathodic Disbondment.
There are a number of International Standards that define the Disbondment test, however the use of a Reference Electrode is common to all.*
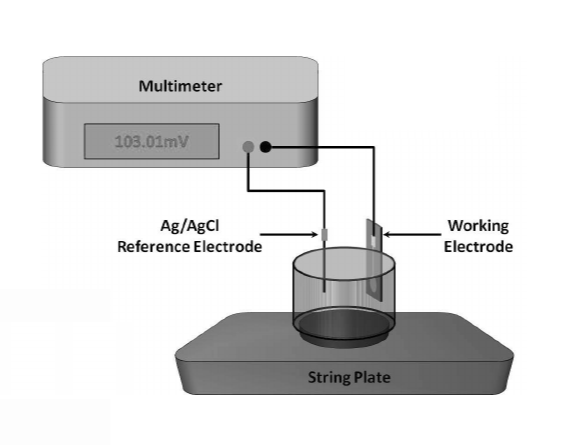
The Disbondment Test Cell is basically a transparent bottomless tube sealed onto the surface of the Pipe or tank in question. The tank is filled with Electrolyte and two electrode half cells are inserted into the tube to complete the set up. One is the counter electrode which may be Platinized Titanium, Platinum or another inert conductor. The other is the reference electrode, this may be one of three types:
Calomel (Mercury/Mercury Chloride Electrode. (Hg/HgSo4)
Copper Sulphate Reference (Cu/CuSO4)
Silver/Silver Chloride Reference (Ag/AgCl)
Here is a Typical Set up:
EDT manufacture and supply all types for the Cathodic Disbondment test.
*DIN Norm 30670, DIN EN ISO 15711, ISO 21809 Part 1 Annex H, ASTM G-8, ASTM G-42.G-95.
Visit Our YouTube Channel for more information about corrosion.
